Electrodialysis (ED) is a very versatile technology for the separation of difficult mixtures. Gu→o Chu technology (Xiamen) Co., Ltd. offers e★xpertise in electrodialysis R&D as well as in the engineering and con→struction of ED systems for the laboratory, piloting, and production.
What is Electrodialysis (ED)?
Electrodialysis is an electromembrane process in which ≈ions are transported through ion permeable membranes from one solution to another u♣nder the influence of a potential gradient. The electrical charges on the ions allow them toγ be driven through the membranes fabricated from ion exchange poly©mers. Applying a voltage between two end electrodes can generate" the required potential field. Since the membranes used in electro↕dialysis have the ability to selectively transport ions having positive or negativ↕e charge and reject ions of the opposite charge. Therefore, elec trodialysis can achieve effective concentration, removal o'r separation of electrolytes.
The ion exchange membranes used in electrodialysis are essentially sheets of ion-exchangeγ resins. They usually also contain other polymers to improve mecha×nical strength and flexibility. The resin component of a cation-exchange membrane would have neg↓atively charged groups (e.g., -SO3–) chemically attached to the polymer chains (e.g., styrene/divinylbenzen♥e copolymers). Ions with a charge opposite to the f>ixed charge (counter ions) are freely exchanged at these sites. The concentration of counter ion©s (e.g., Na+) is relatively high, therefore, counter ions carry most of the el ectric current through the membrane. The fixed charges attached to the polymer chains repel ions of the same charge (co-ions), in this case the anions. Since their concentration in the membrane is relatively low✔, anions carry only a small fraction of the electric current through a® cation permeable membrane. Attachment of positive f<ixed charges (e.g., -NR3+ or C5H5N+R where commonly R = CH3) to the polymer chains Ωforms anion exchange membranes, which are selective to transpo$rt of negative ions, because the fixed -NR3+ groups repel positive ions. This exclusγion, as a result of electrostatic repulsion, is called Donnan exclusi±on.
Ion-exchange polymers such as poly(styrene sulfonic acid) are water soluble, so crosslink>ing is needed to prevent dissolution of ion permeable membranes. Divinylbenzene is used to cross link polystyrene chains. The degree of cross-linking and the fixed-charge dens≈ity affect the membrane’s properties in opposite w®ays. Higher crosslinking improves selectivity and membrane sta&bility by reducing swelling, but it increases electrical resistance. ←High charge density reduces resistance and increases ×selectivity, but it promotes swelling and thus necessitates higher crosslinking. A compromise> between selectivity, electrical resistance, and dimensional stability is achieved by proper aφdjustment of crosslinking and fixed-charge densities.
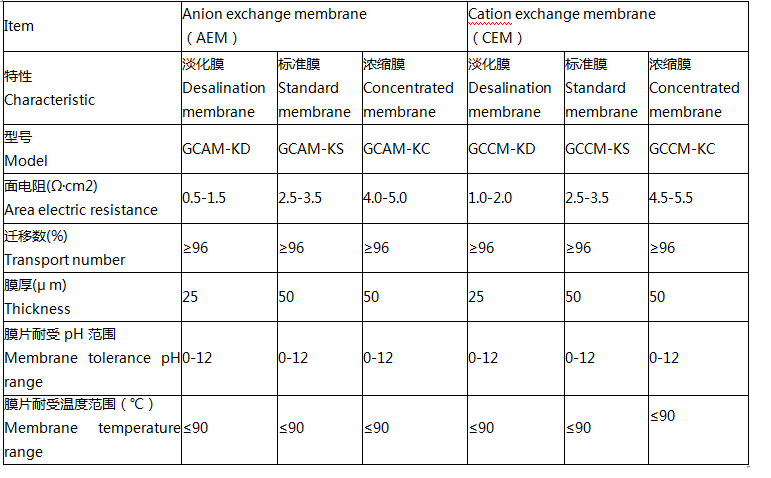
Product parameters
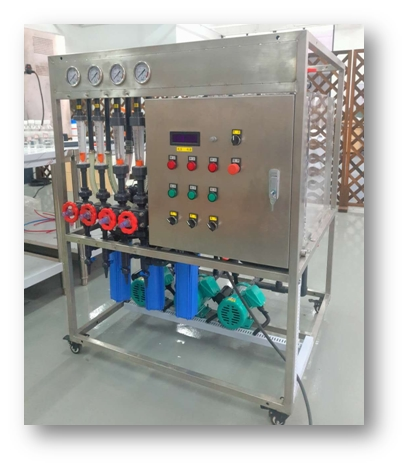
The following are our electrodialysis modules from small to indus✘trial scale.

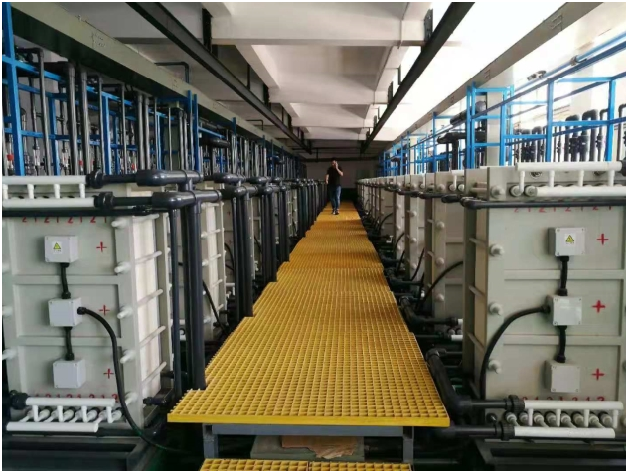
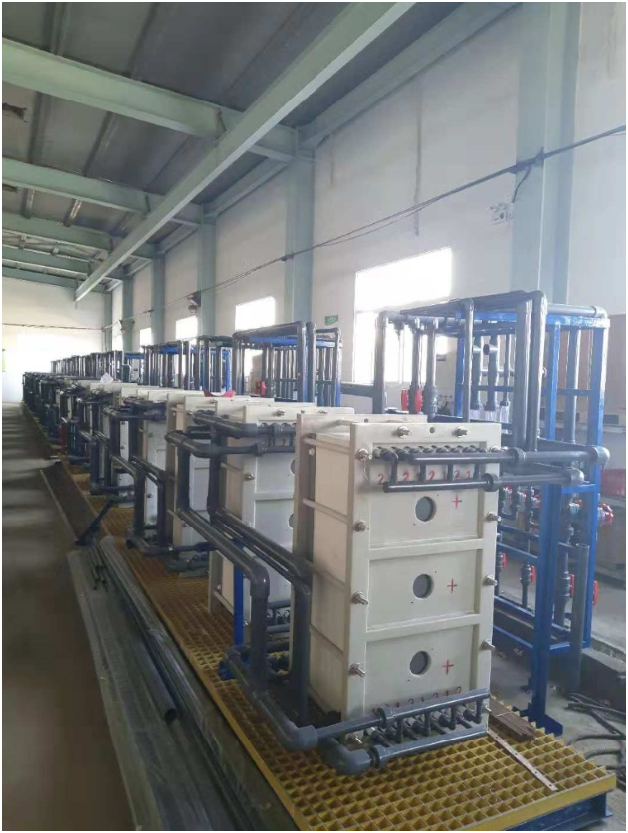
We can also provide complete sets of experimental and industr♦ial devices.



 Ion Exchange Membranes Applications
Reduce Electrolyte Content:
Ion Exchange Membranes Applications
Reduce Electrolyte Content:
Potable from brackish water
Food products – whey, milk, soy sauce, fruit juice
Nitrate from drinking water
Cooling tower water
Boiler feed water
Rinse water for electronics processing
Electroless plating baths
Recovery of blood plasma proteins
Pickle brines to recover flavor
Sugar and molasses
Amino acids
Potassium tartrate from wine
Chloride purge in Kraft paper process
Photographic developer regeneration
Fiber reactive dyes
Recover Electrolytes:
Pure NaCl from seawater
Ag(I) salts from photographic waste
Ni(II) from electroplating rinse water
Zn(II) from galvanizing rinse water
Salts of organic acids from fermentation broth
Amino acids from protein hydrolysates
Acids from metal pickling baths and rinse
HCl from cellulose hydrolysate
Miscellaneous:
Salt splitting
Metathesis
Concentrate reverse osmosis brines
Ion substitution
As you can see, the ion exchange membranes have a wide range of applications in many¶ fields. Our experience with ion exchange membranes can help you determine whether it is the approp≠riate technology for your needs.
Contact:
Tel:+86 592 6514970
Email:market@guochukeji.com
Skype:18060902001
WhatsApp:18060902001
WeChat:18060902001
TM: 18060902001
QQ:1641011431