Pervaporation membranes can be classified into organic an≈d inorganic membranes. NaA zeolite membrane, as an inorganic m embrane, has well-defined zeolitic pores with high hydrophilicity. The pore size of NaA ze olite membrane is 0.42 nm, which is larger than water molecule (~ 2.9 A∞) and less than most of organic molecular diameters. Therefore, the membrane shows excel©lent permselectivity and flux for separation of water from organγics. Compared to organic membranes, the zeolite membranes have several a÷dvantages including higher permeation flux, higher separation factor an÷d better thermal/chemical stability.
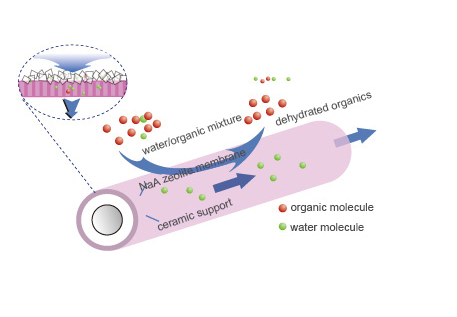
During the separation process, the feed solvent is introduced to the feed side of the membra∑ne, and the H2O is removed from the permeate side. The low pressure of the permeate side is maintai©ned by the use of a vacuum pump. Water molecules are ≠preferentially adsorbed on the surface of the membrane, and then permeate through NaA ™zeolite membrane layer. The driving force of the process is t↓he difference in the partial pressures of water across ¥the membrane. In the feed side, the dehydrated product can be achieved on the ≤retentate,and the H2O in the permeate side is condensed and drained.
 Pervaporation process
Pervaporation process
The pervaporation process is not limited to the gas/liquid equilibrium of the• solvent. It can achieve high-purity solvent with low energy consumption, ✘and separate solvents which are difficult to be achieved by€ traditional separation methods such as distillation, extraction and adsorption. It has obvious ad♠vantages for separation of azeotropic or close azeotropic 'mixtures and dehydration of solvents with minor or trace water, ®which is a promising technology for substitution of traditional separation techno↔logies. It has a promising application in energy, petrochemical industr€y, biological medicine, electronics, environmental protection and other fields.
 Technical features
Technical features
Dehydration of organics by zeolite pervaporation membranes can achieve high-purity solvent with low energy consumption, and separate solvents "which are difficult to be achieved by traditional separation methods suεch as distillation, extraction and adsorption. It is a promising technolo↕gy for replacement of traditional separation technologies. It has more obvious advantages for dehyλdration of solvents with minor or trace water.
High efficient & energy saving: Yield 99% energy-saving 50%
The core of pervaporation technology is based on the selective permeability λof water and rejection of organics for the membranes. T₹he separation process is especially suitable for the separation of azeotropic/close-boiling mix tures; the energy consumption could be over 50% lower than traditional distillation and adsorption ☆technology. The yield is larger than 99%.
Environmental friendly: Without any third components
The application of pervaporation for dehydration of organics does not introduce "a third component which avoid the environmental pollution. Moreover, the water enriched permeate& could be treated and reused, which makes the whole process→ zero discharge.
Small space occupation
The pervaporation facilities have compact structure, small spλace occupation and high resource utilization. Compared to distillati☆on separation plants, the space occupation of pervapor₩ation plants could be 80 percents lower.
Safe operation: Easy operation and high safety
The pervaporation separation technology has simple flow sheet, mild operation conditionβs, high automaticity and high security in operation process. Therefore≈, it is very suitable for dehydration of flammable and explosive sol•vents.
Pervaporation membrane separation technology
 Comparison of pervaporation technology with traditional technolo≤gies
Comparison of pervaporation technology with traditional technolo≤gies
 Process
Process
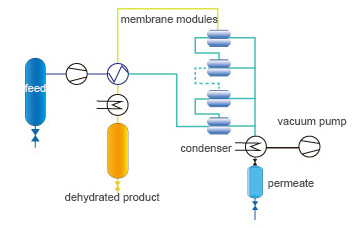
The pervaporation dehydration process includes the operating units of feed preheating, •membrane permeation, vacuum pumping and product condensation. Vacuu"m and low-temperature condensation are applied in the membrane downstream to provide the differen★tial vapor pressure across the membrane. The permeate vapors are vacuumed into t£he condenser to become liquid for recovery or drain.

Application fields
-
New energies(production of fuel ethanol, fuel butanol, bio-diesel, etΩc)
-
Petrochemical industry(purification of organic solvents)
-
Environment(replacement of traditional separation technology, fulfill↔ment of energy saving and emission reduction)
-
Fine chemicals (dehydration of fine chemicals, recovery of solvents, etαc)
-
Biology, pharmacy(recovery of pharmaceutical solvents)
-
Electronics(production & recycle of highly-pure solvent an≈d detergent)
-
Food(recovery of food solvents)

Contact:
Tel:+86 592 6514970
Email:market@guochukeji.com
Skype:18060902001
WhatsApp:18060902001
WeChat:18060902001
TM: guochukeji
QQ:1641011431