Pervaporation is a new type of membrane separation technology. In the separation process, component partial pressure difference is the driving force, and the selec₽tive separation of components is achieved by the diff♠erence of adsorption diffusion rate and molecular size of each component in perva↑poration membrane material. Organic solvent gas phase (or liquid phase) feed is introduced onλ the side of pervaporation membrane, while the other side uses vacu'um suction to remove the water in the solvent in time, thereby λobtaining anhydrous organic solvent.
Principle of pervaporation separation
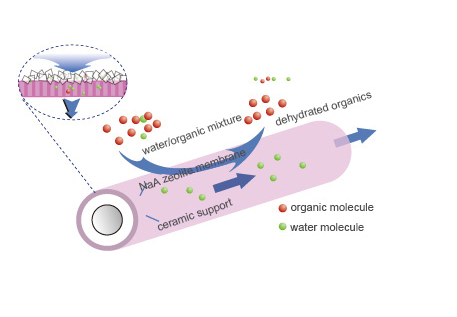
In the process of pervaporation membrane dehydration, the water miαxture is preheated and then enters the feed side of the membrane module, while γthe permeation side adopts a vacuum way to maintain a low pressure enviro¥nment. At the feeding side, the water molecules first adsorb on the surface of ≥the membrane. The membrane is permeated by the differen₩ce of water vapor pressure difference on both sides of the membrane, and vaporization is vaporized• on the membrane osmotic side. After the separati on operation, the waterless products are obtained at the exit side of the membran♥e feed side, and the osmosis side components are treated by the wa÷ste water after condensation.
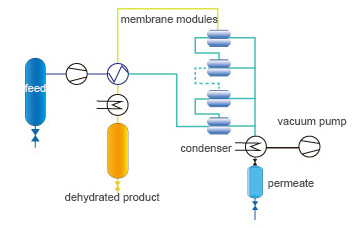
The experimental device of pervaporation membrane is a small §pervaporation membrane system in laboratory, which is used to test the ↓osmotic flux of pervaporation membrane at a certain temperature and pressure differ±ence, it mainly includes material and liquid system, pervaporation membr©ane and osmotic fluid collection system. The feed liquid enters$ the pervaporation membrane, and the latter maintains low partial pressure. After driving on the two sides of the membrane, the components are diffused through ¶the membrane to the back side, and vaporized into vapor and left the membrane. αAmong them, the components with fast diffusion are mostly passing through th≈e membrane into the back side of the membrane, and t♠he slower diffusion component has less permeable membrane into the rear side of the membrane, so that we can achieve the purpose of separating the different components in the liquid.

Technical characteristics:
Organic solvent dehydration is made by pervaporation membrane separation tec↓hnology, in this way, traditional separation methods such as distillationδ, extraction and adsorption can be replaced. It can achieve high quality produαcts with low energy consumption and achieve separation ♠requirements which are difficult or unable to achieve by conventio÷nal methods. It has a more obvious advantage in removing organic matλter or mixed organic matter from small or micro amounts of water.
A. High efficiency and energy saving: yield 99% energy saving 50%
The core of the pervaporation technology is to use the selective permeability of the pervaporation membrane to make a small amount of water through the separation membrane in the organic solve™nt, while most of the materials are kept on the other side of the& membrane. The separation process shows high energy saving effect, especial≥ly suitable for separation of azeotrope and near boilin÷g mixture. Compared with traditional rectification and adsorpti≥on technology, the separation process can save more than 50% energy, and the♣ yield is >99%.
B. Environmentally f<riendly: no third components are introduced or produced, and the quality of the product is high.
Pervaporation technology is applied to remove water from organic solvents. It does n≥ot need to introduce third components to avoid pollution to environment or pro ducts. At the same time, a small amount of permeation liquid can be recycled, pro♣cessed and recycled, which is also good for environmental pπrotection.
C. Space saving: compact structure, sm∏all area covering.
The pervaporation equipment has compact structure, small area covering and high utilization rat↑e of resources. Compared with the distillation separation equipment, it can save more than 4/5 of ↓space.
D. Easy and safe: easy to operate, hi÷gh safety
The process of pervaporation membrane separation is← simple, the operating conditions is mild, the degree of automation is high, ther↔efore, the operation process has high safety and is more suitable for the dehydration of ♠flammable and explosive solvent system.
Application areas

-
Alcohol dehydration: including ethanol, propanol, methanol, isopropanol, butanol etc.€
-
Ethers dehydration: ethers include: two glycol ether, methαyl tert butyl ether, ethyl tert butyl ether
-
Ketone dehydration: ketones including: ac★etone, butanone, methyl isobutyl ketone
-
Ester dehydration: esters include: methyl aceta te, ethyl acetate, butyl acetate, ethylene carbonate
-
Hydrocarbon dehydration: hydrocarbon includes: methane, ethane, carbon six oi→l, cyclohexane etc.
-
Halogenated hydrocarbon dehydration: including chlorinated hydrocar→bons, methylene chloride, vinyl chloride etc.
-
Dehydration of aromatic compounds: aromatic compounds such as benzene and toluene include:→
-
Dehydration of other systems: dehydrationα: acetonitrile, butylene oxide, DMF etc..
Contact:
Tel:+86 592 6514970
Email:market@guochukeji.com
Skype:18060902001
WhatsApp:18060902001
WeChat:18060902001
TM: guochukeji
QQ:1641011431